.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
What is REMS?
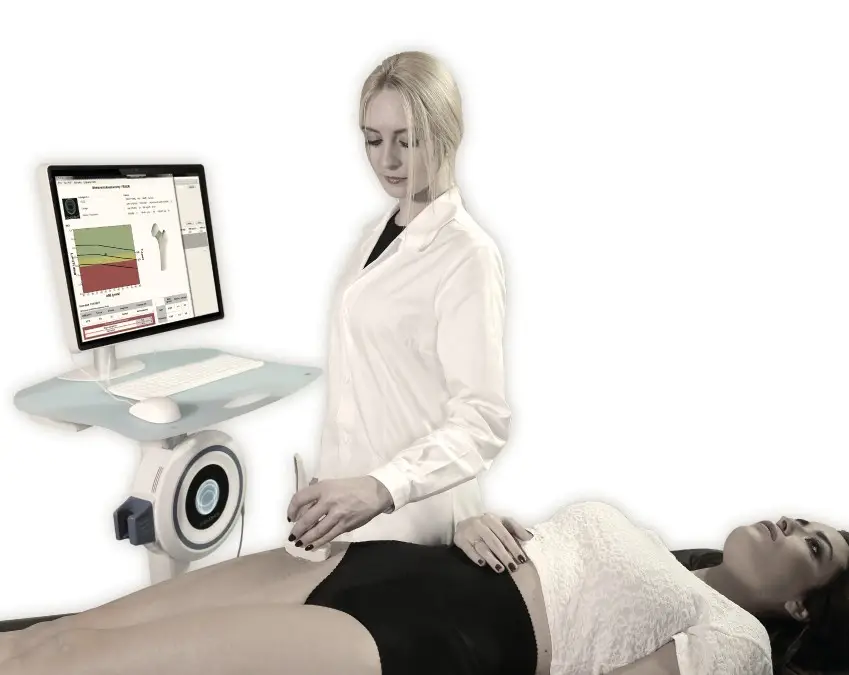
REMS (Radiofrequency Echographic Multi-Spectrometry) is a cutting-edge, radiation-free technology that uses advanced ultrasound to assess both bone density and bone quality. Unlike traditional methods like DXA, REMS provides a clearer, more comprehensive understanding of your bone health by evaluating not just the mineral density but also the internal structure of your bones. This dual approach offers a more accurate assessment of fracture risk and bone strength.
Key Benefits of REMS Technology:
- Radiation-Free: Safe for all, including pregnant women and cancer patients.
- Comprehensive: Measures bone density and quality for a complete picture.
- Accurate: Detects changes in bone density of less than 1%, ensuring reliable results.
- Immediate: Provides results in minutes, so you can take action quickly.
How Does REMS Work?
By leveraging advanced radiofrequency signal analysis, REMS delivers highly accurate, reliable, and radiation-free insights into your bone health, making it a groundbreaking tool for early detection and prevention.
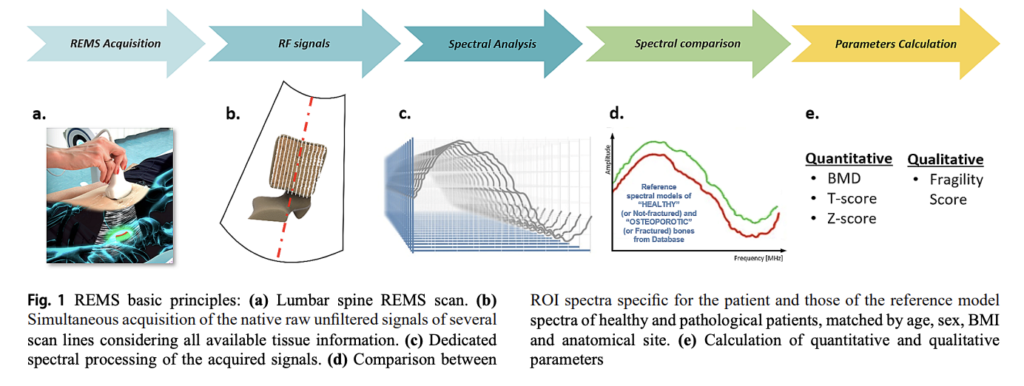
Here’s how it works:
- A small device called a transducer emits sound waves to the targeted bone area.
- These sound waves bounce back (echo) from the bone and are captured by the transducer.
- The collected data is used to create detailed images of the bone, including important structures like individual vertebral bodies, the femoral neck, femoral head, and greater trochanter.
- Specialized software analyzes the signals to assess bone density (BMD) and bone quality, providing a complete picture of bone health.
REMS goes beyond traditional scans by analyzing the internal bone microarchitecture. It compares the results to reference populations (both “normal” and “osteoporotic”) and calculates key measurements, such as T-scores, Z-scores, and fragility scores. These outputs are comparable to what you would receive from a DXA scan, but with greater precision and the added benefit of assessing bone quality.
Bone Strength and Microarchitecture
Bone strength is the ability of your bones to resist fractures, determined by four key components: composition, microarchitecture, size, and shape. Each of these factors plays a unique role in maintaining strong, healthy bones:
- Composition: Includes bone minerals, cellular density, and collagen quality, all of which contribute to bone toughness at a microscopic level.
- Microarchitecture: Refers to how bone tissue is structured, including the arrangement of trabeculae (tiny rods in spongy bone) and the porosity of cortical bone. Strong microarchitecture helps bones handle stress and reduces fracture risk.
- Size and Shape: External features of bones, influenced by genetics, age, and lifestyle, which impact their ability to absorb and distribute force effectively.
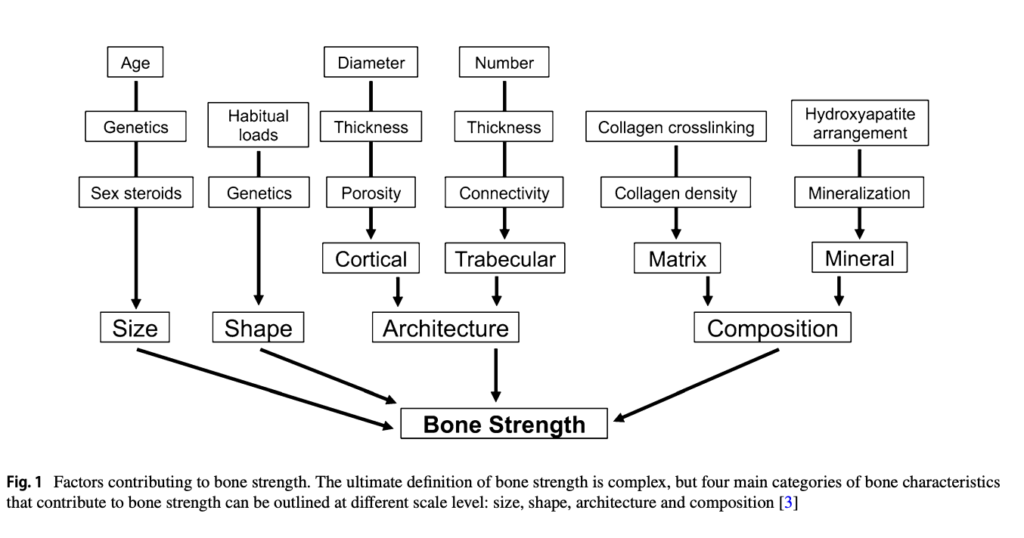
Why Microarchitecture Matters
Bone density alone doesn’t give the full picture of bone health. While it measures mineral content, it doesn’t account for structural strength or how the bone remodels itself over time. Poor microarchitecture can make bones fragile, even if density appears normal.
- Predicting Fractures: Research shows that evaluating microarchitecture offers better insights into fracture risk than density alone. Bones with healthy microarchitecture are more resilient, even with moderate density levels.
- Aging and Fragility: As bones age, microarchitectural changes like increased porosity and reduced connectivity can weaken them, making fracture risk harder to predict with traditional scans.
The Fragility Score: A Game-Changer in Bone Health
The Fragility Score is a unique feature of REMS that evaluates bone structure independent of density. Using advanced ultrasound analysis, it identifies weaknesses in the bone’s microarchitecture and calculates a score from 0 (normal structure) to 100 (high fragility).
- How It Works: REMS analyzes sound waves reflected from the bone and compares the data to a reference database of fractured and non-fractured bones. This approach helps identify skeletal fragility with unparalleled accuracy.
- Why It’s Effective: The Fragility Score predicts fracture risk over five years, helping patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about prevention and treatment.
- Validated Precision: Studies have confirmed the Fragility Score’s accuracy in predicting fractures, often outperforming traditional methods like DXA.
How is REMS Different from a DEXA Scan?
While DXA scans have been the traditional standard for bone health, they come with limitations that REMS overcomes. Here’s how REMS stands out:
- No Radiation: REMS uses ultrasound, eliminating the risks associated with low-dose X-rays in DXA scans.
- Bone Quality Assessment: REMS evaluates both bone density (T-scores) and quality (Fragility Score), offering a more accurate picture of fracture risk.
- Fewer Limitations: REMS scans are unaffected by conditions like osteoarthritis, spinal deformities, or hardware from previous surgeries, which often skew DXA results.
- Enhanced Precision: DXA scans require a two-year interval to detect changes, while REMS can detect subtle changes in bone density of less than 1%, allowing for more frequent monitoring.
- Fewer Errors: REMS eliminates positioning and interpretation errors commonly associated with DXA scans.
Why Choose REMS Over DEXA?
REMS provides advanced insights into your bone health, empowering you to take proactive steps before a fracture occurs. Whether you’re managing osteoporosis, monitoring early bone changes, or seeking an alternative to radiation-based scans, REMS is the clear choice.
Causes of Inaccuracies in DEXA
Several factors can result in inaccurate results from DEXA scans.
Changes in positioning of patient
The way the DEXA technician positions your body for each scan can affect your results.
Patient movement
If you move your body during a DEXA scan, this can significantly impact the results.
DEXA machine calibration
DEXA machines require regular calibration. If a machine hasn’t been properly calibrated, this can affect your results.
Inadequate hydration
Your hydration levels affect your soft tissue’s density which can affect the absorption of the X-rays of a DEXA.
Clothing worn during the DEXA scan
Research shows that various textiles affect the DEXA scan, resulting in inaccurate results.
Bone spurs, osteoarthritis and scoliosis
DEXA cannot tell the difference between these variations within your bone, so they can skew the results of your DEXA scan.
How Will REMS Change Bone Health Monitoring?
REMS technology represents a groundbreaking shift in how we assess and monitor bone health:
- Proactive Care: Early detection of bone quality issues allows for preventative action, reducing the risk of fractures.
- Personalized Insights: Fragility Scores help tailor lifestyle, diet, and treatment plans to individual needs.
- Frequent Monitoring: With the ability to detect subtle changes in bone health, REMS makes it easier to track the effectiveness of treatments or lifestyle modifications.
- Empowering Clients: By providing immediate, detailed results, REMS removes fear and replaces it with actionable knowledge, giving clients control over their bone health journey.
Doctor Testimonials


Take Action Now!
Don’t wait until a fracture occurs to take action. With REMS, you can stay ahead of potential issues and build a future of strength and resilience. Book your scan today and take the first step toward better bone health.
